Copper ore processing is not a single-machine job. From crushing to concentration, every step plays a key role in ensuring high recovery, stable output, and low operating costs.
If you’re new to copper mining or planning to start a processing plant, this guide will give you a clear, easy-to-understand overview of the full production process.
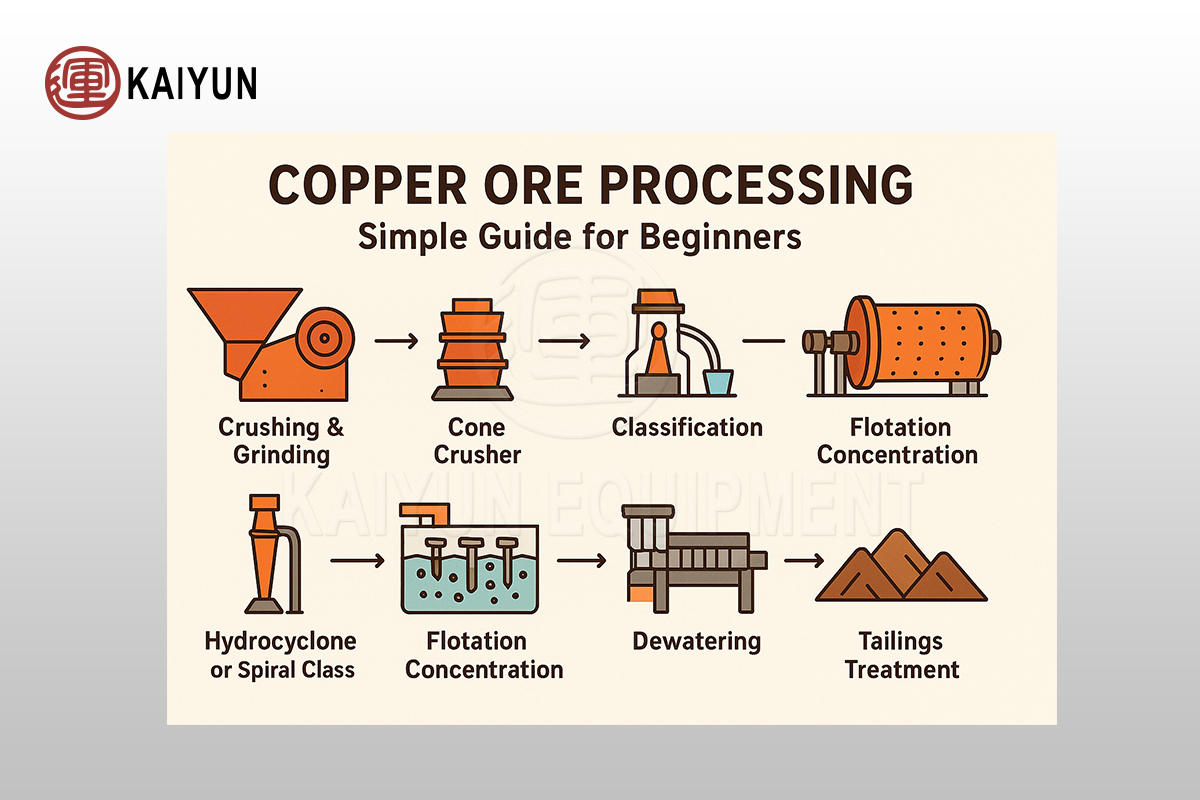
1. What Is Copper Ore Processing?
Copper ore processing refers to transforming raw copper ore from the mine into a high-grade copper concentrate.
It involves multiple stages—each designed to remove waste rock and enrich the copper content.
Common copper ores include:
Copper sulfide ore (Chalcopyrite, Bornite)
Copper oxide ore (Malachite, Azurite)
Mixed copper ores
Different ores require different process flows, but the core steps remain similar.
2. Core Process Flow of Copper Ore Processing
Step 1: Crushing & Grinding – Prepare the Ore for Separation
Raw copper ore is first reduced in size through:
Jaw Crusher
Cone Crusher
Vibrating Screen
Then they enter ball mills for fine grinding.
Purpose: Liberate copper minerals from the host rock.
Step 2: Classification – Control Particle Size
After grinding, the slurry goes into:
Hydrocyclones
Spiral classifiers
This ensures only properly sized particles enter the next separation stage, improving recovery.
Step 3: Flotation – The Core of Copper Recovery
Flotation is the most widely used method for copper sulfide ores.
Equipment includes:
Flotation cells / flotation machines
Mixing tanks
Air blowers
Through reagents and aeration, copper attaches to bubbles and rises to the surface, forming a concentrate foam layer.
Advantages:
✔ High recovery rate
✔ Suitable for large-scale production
✔ Effective for low-grade ores
Step 4: Concentrate Thickening & Dewatering
The copper concentrate from flotation contains water. It needs to be thickened and filtered with:
Thickeners
Filter presses
Rotary dryers (optional)
Final product: Copper concentrate (20–35% Cu) suitable for smelting.
Step 5: Tailings Treatment & Environmental Protection
Tailings are processed in:
Tailings thickeners
Dry stack tailings systems
This reduces water loss and protects the environment while meeting regulations.
3. Typical Copper Ore Processing Plant Layout
A standard copper processing line includes:
Feeding system
Primary & secondary crushers
Flotation line
Concentrate dewatering system
Tailings treatment
This full set ensures stable production and high recovery.
4. How to Choose Equipment for Your Copper Project?
When designing a copper processing plant, consider:
Ore type (sulfide / oxide / mixed)
Copper grade
Capacity demand (tons per hour)
Power & water availability
Budget level
Required concentrate grade
For copper oxide ores, the flow may include leaching, solvent extraction, and electrowinning (SX-EW) instead of flotation.
5. Why Complete Processing Systems Matter
Many beginners believe one or two machines are enough.
In reality, a complete system is essential for:
✔ Stable production
✔ High recovery
✔ Low cost per ton
✔ Longer equipment lifespan
✔ Easier operation & maintenance
A well-designed copper processing line can determine the success of your project from day one.
6. Conclusion
Copper ore processing requires a coordinated set of equipment and a scientific process flow. From crushing to flotation and dewatering, each step affects the final recovery and output.