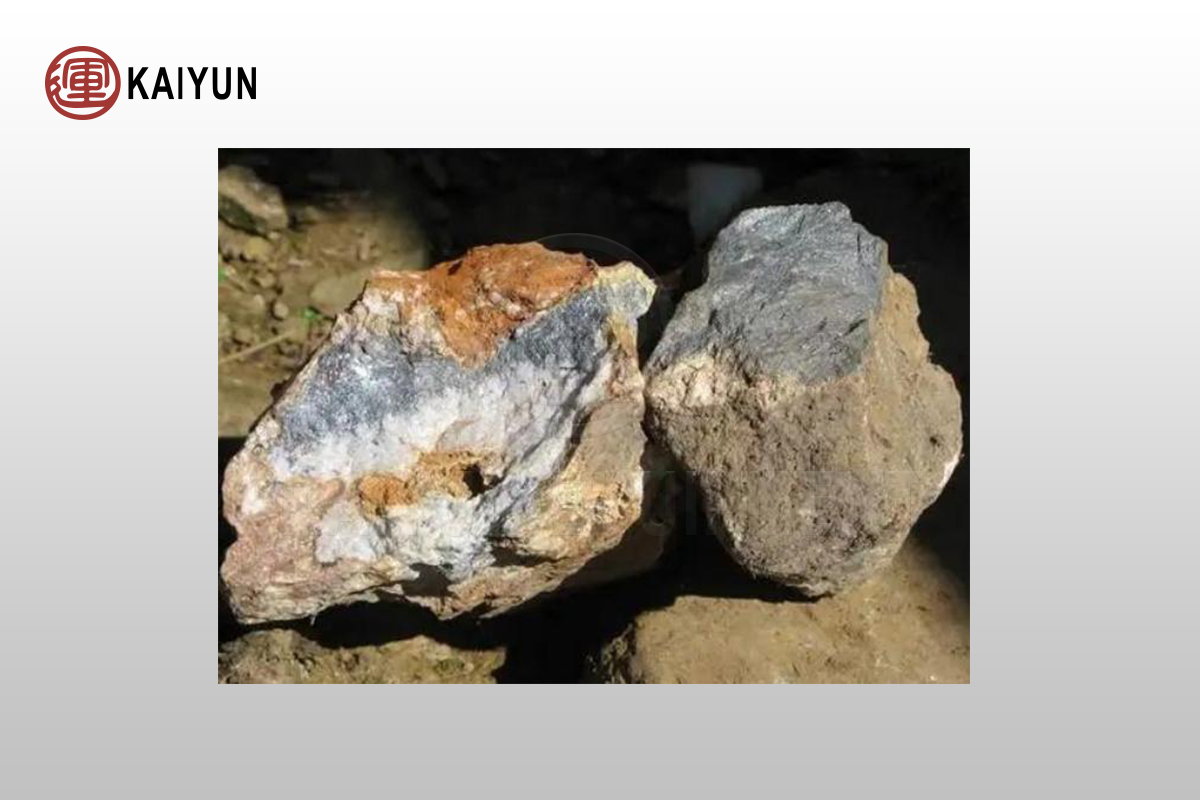
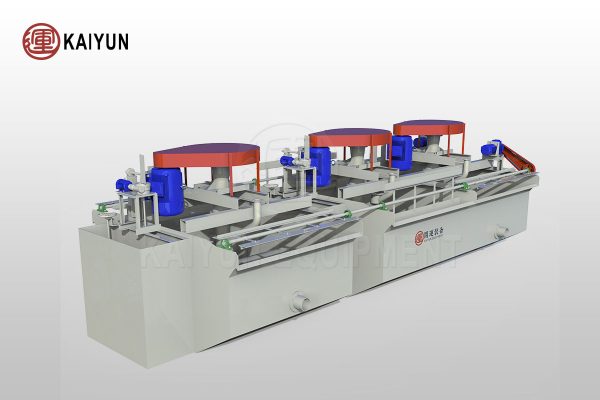
How to choose the appropriate sulfide gold ore dressing process?
High sulfide gold ores often contain a large amount of pyrite, arsenopyrite and other sulfide minerals. The gold grade is usually low, and the gold particles are small and tightly wrapped by sulfide minerals, making it difficult to recover directly through the cyanidation method. For this type of gold ore, flotation technology is an economical and effective choice. Through flotation, gold can be enriched in copper, lead, sulfur and other concentrates, and then gold can be extracted from them, which not only improves the gold recovery rate, but also realizes the comprehensive utilization of multiple metals.
Antimony Oxide Beneficiation Process
The beneficiation process of antimony oxide needs to select a suitable method according to the properties of the ore (such as mineral composition, embedded particle size, associated impurities, etc.). The core process includes crushing and screening, gravity separation/flotation separation and tailings treatment.
Commonly Used Flotation Methods For Antimony Ore
Antimony is an important non-ferrous metal, widely used in flame retardants, alloy additives and electronic semiconductors. Flotation is a key technology to improve the grade and recovery rate of antimony concentrate. For different types of antimony ores, appropriate flotation processes need to be adopted.
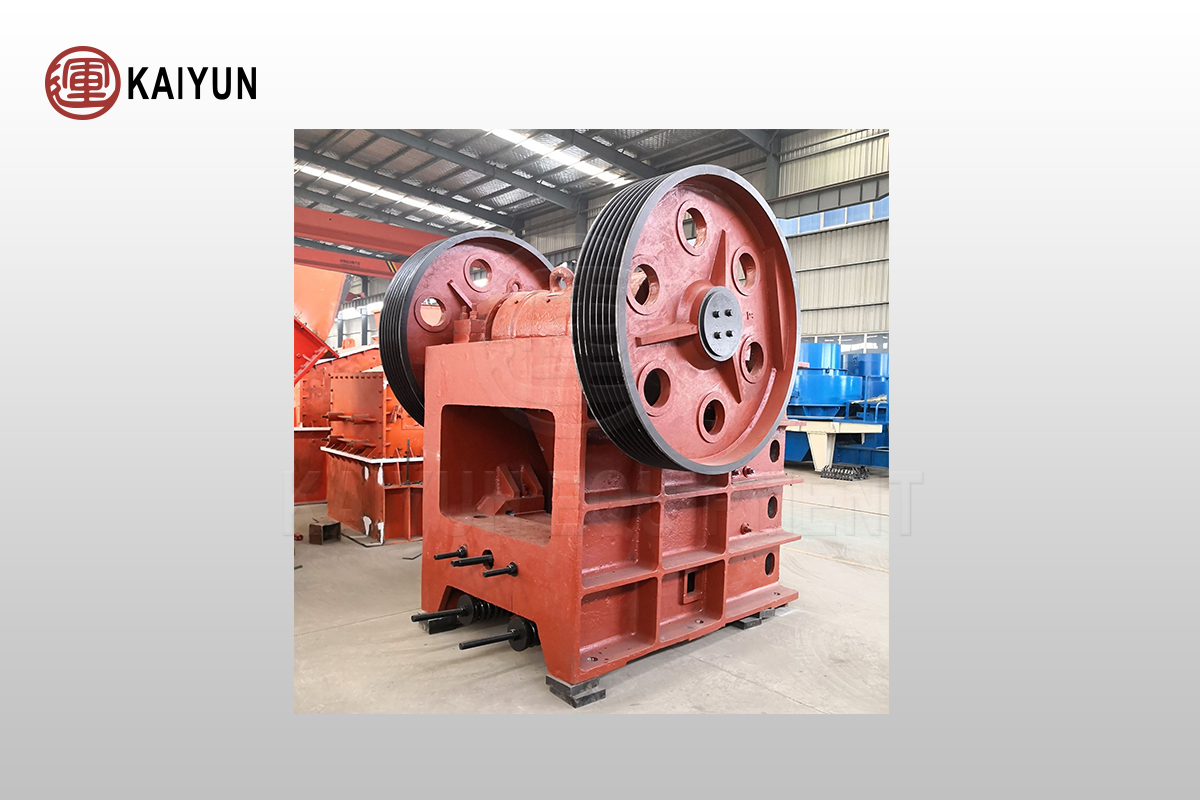
How to solve the problem of uneven jaw crusher discharge
Jaw crusher is a key equipment in the ore coarse crushing process. It is widely used in various ores and rocks with a compressive strength not exceeding 320MPa with its excellent crushing capacity and high efficiency. However, in the actual production process, the jaw crusher may have uneven discharge particle size, affecting the crushing effect and subsequent process flow.
Tailings Treatment and Comprehensive Utilization in Mineral Processing Plants
The world's major mineral producing countries is facing a severe environmental issue—massive tailings accumulation. Tailings are the waste materials left after valuable minerals are extracted from ores. Long-term storage of tailings not only occupies large areas of land but also leads to resource wastage, environmental pollution, and safety risks. However, tailings are not entirely worthless; they still contain valuable components that can be recovered. Proper treatment and comprehensive utilization of tailings are essential.
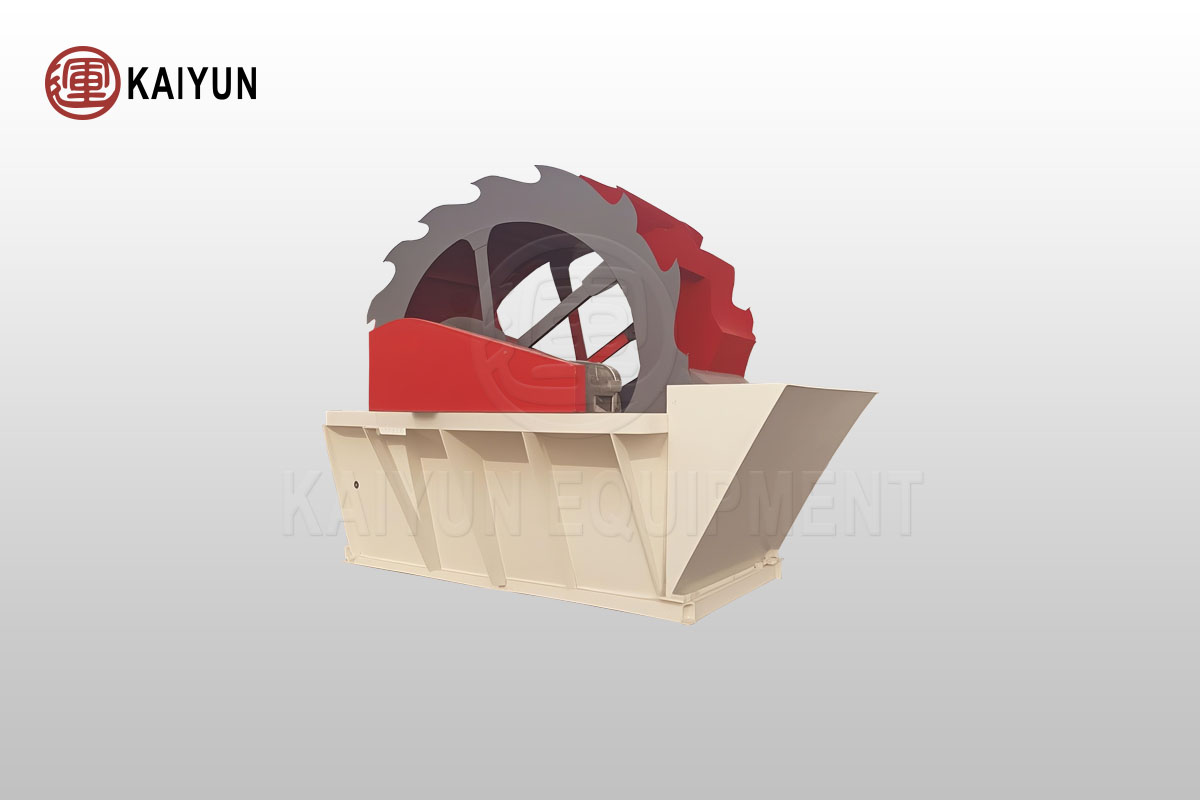
Common Faults and Solutions of Sand Washing Machines
Sand washing machines are as the core equipment for cleaning sand and gravel aggregates, it is widely used in the purification of machine-made sand and natural sand. Through the dual effects of hydraulic impact and mechanical friction, it can effectively remove dirt, dust and other impurities attached to the surface of sand particles, while destroying the water vapor wrapping layer between sand particles, significantly improving the cleanliness and looseness of sand. In production, sand washing machines will inevitably encounter various problems.
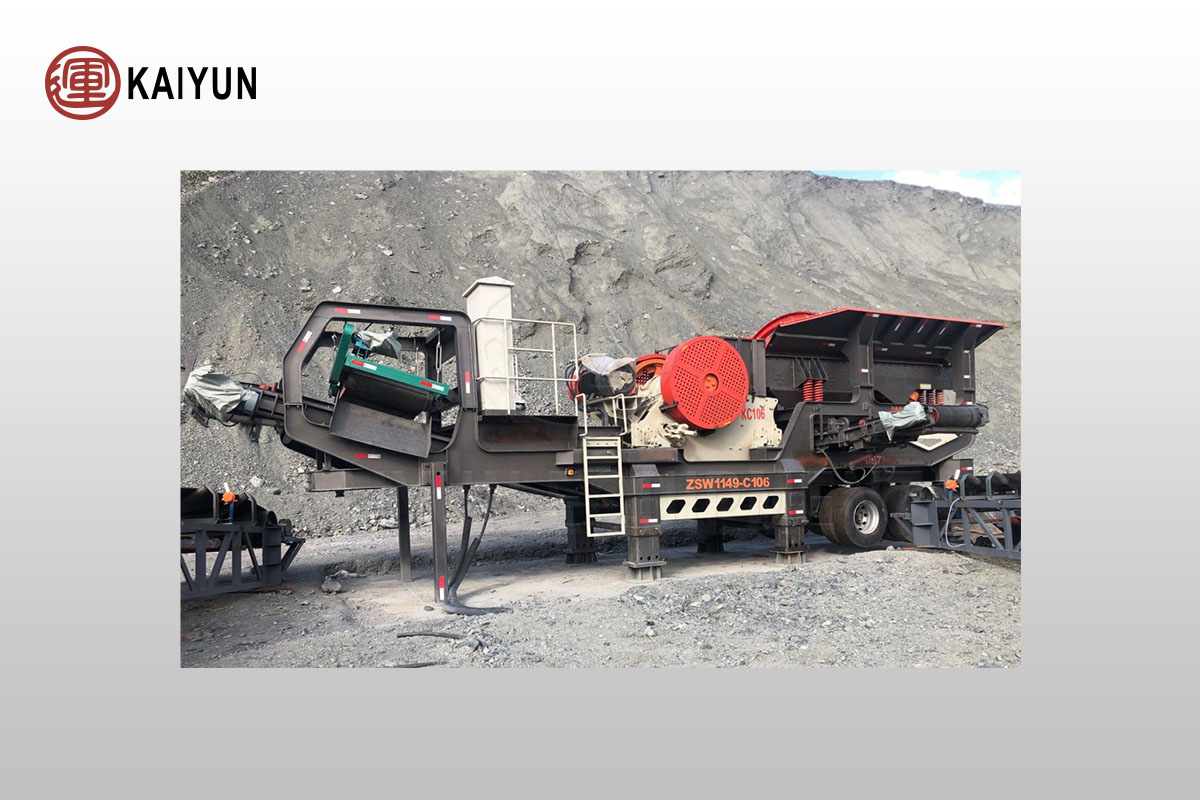
What are the advantages of the mobile stone crusher plant?
Mobile stone crusher plant is divided into coarse crushing, medium crushing and fine crushing according to the size of feed and discharge particles in the crushing operation. It can be equipped with jaw crusher, impact crusher, cone crusher, sand making machine, hammer crusher and other equipment to meet the needs of the majority of users.
Precautions for using tire mobile crushing station
The following key issues should be noted in the daily use of a mobile tire crushing station to ensure efficient operation of the equipment, extend its life and ensure safety
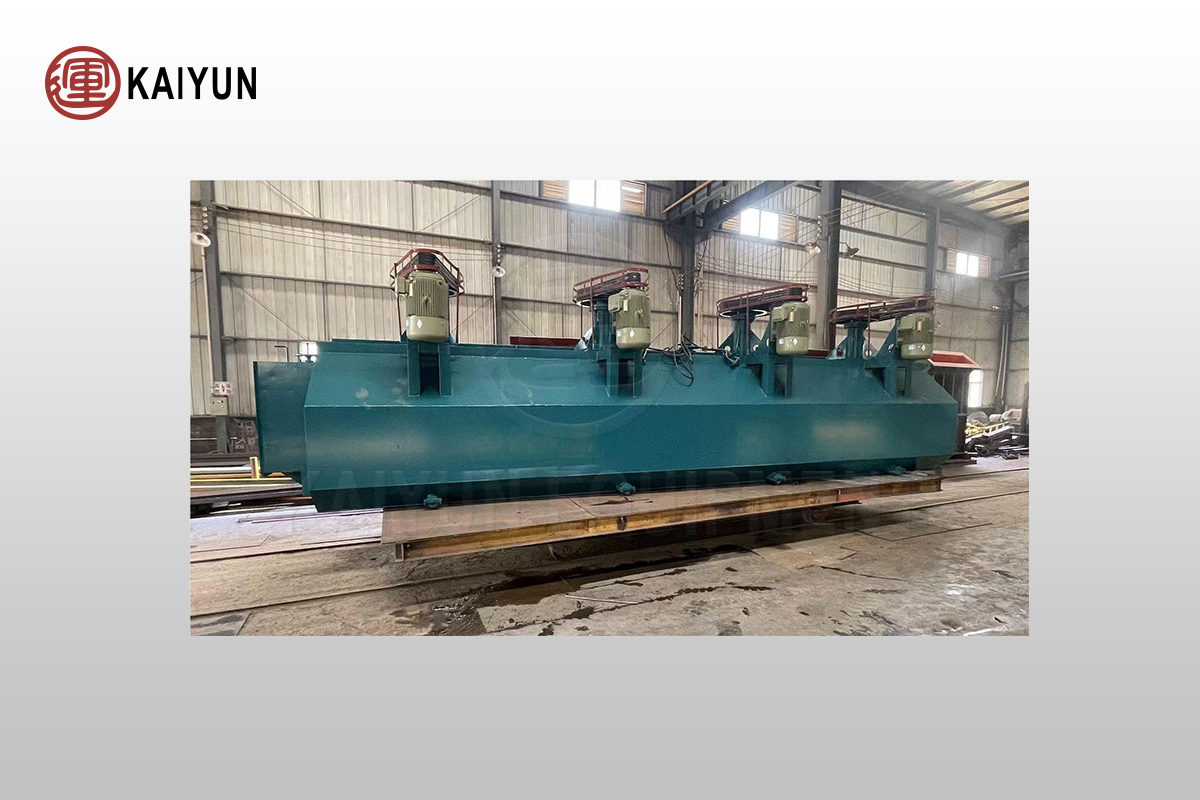
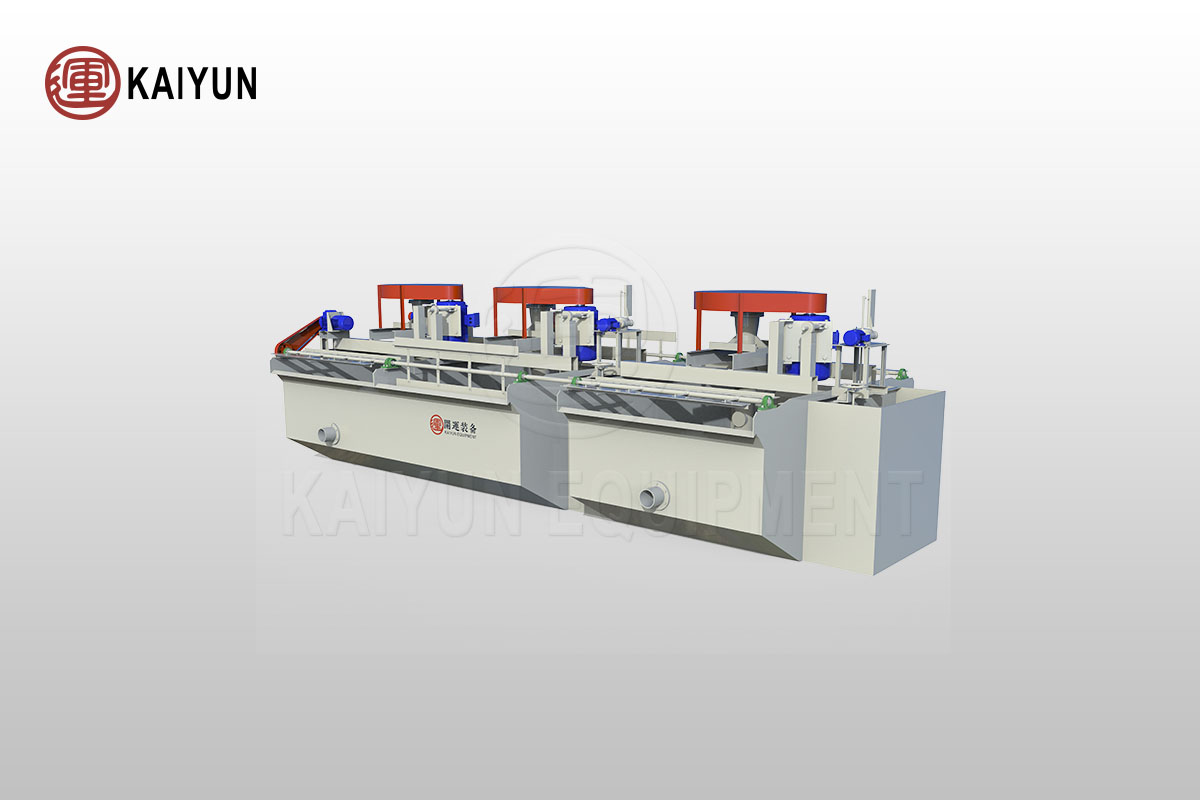
Common Problems and Solutions of Flotation Equipment
Flotation equipment is a key equipment in the mineral processing process, and its operating status directly affects the mineral processing efficiency and product quality.