Introduction to ilmenite
Ilmenite is an oxide mineral of iron and titanium, also known as titanomagnetite, and is the main ore for refining titanium. Ilmenite is heavy, gray to black, and has a little metallic luster. The crystals are generally plate-shaped, and the crystals are gathered together in blocks or granules. The composition is FeTiO3. The TiO2 content is 52.66%, and it is the main mineral for extracting titanium and titanium dioxide.
Ilmenite (FeTiO₃) is an important titanium resource and is widely used in the production of titanium dioxide, titanium metal and titanium alloys. It usually coexists with magnetite, rutile and quartz. The mineral processing process needs to make full use of the specific gravity difference, magnetic difference and surface chemical properties of the mineral.
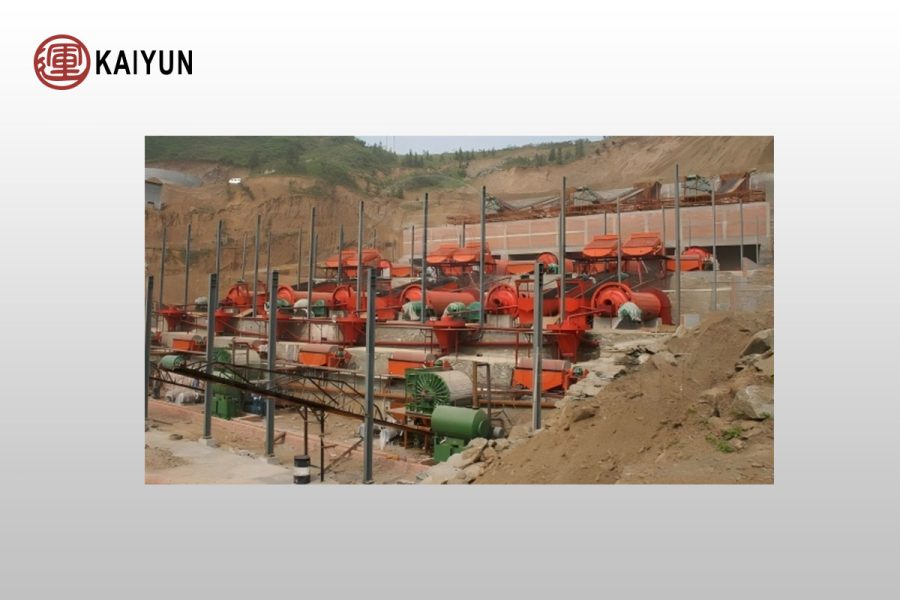

Table of Contents
Commonly used beneficiation process
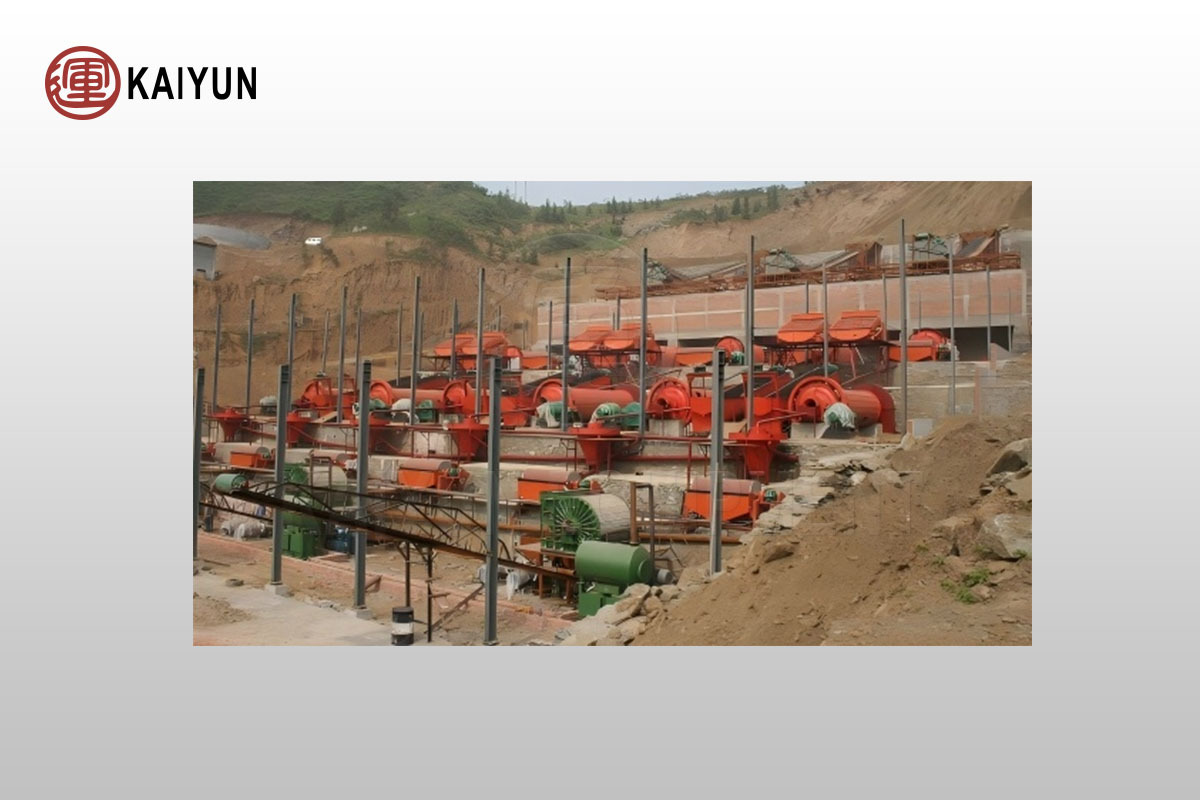
The beneficiation process of ilmenite mainly includes crushing, grinding, gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation and combined beneficiation, as follows:
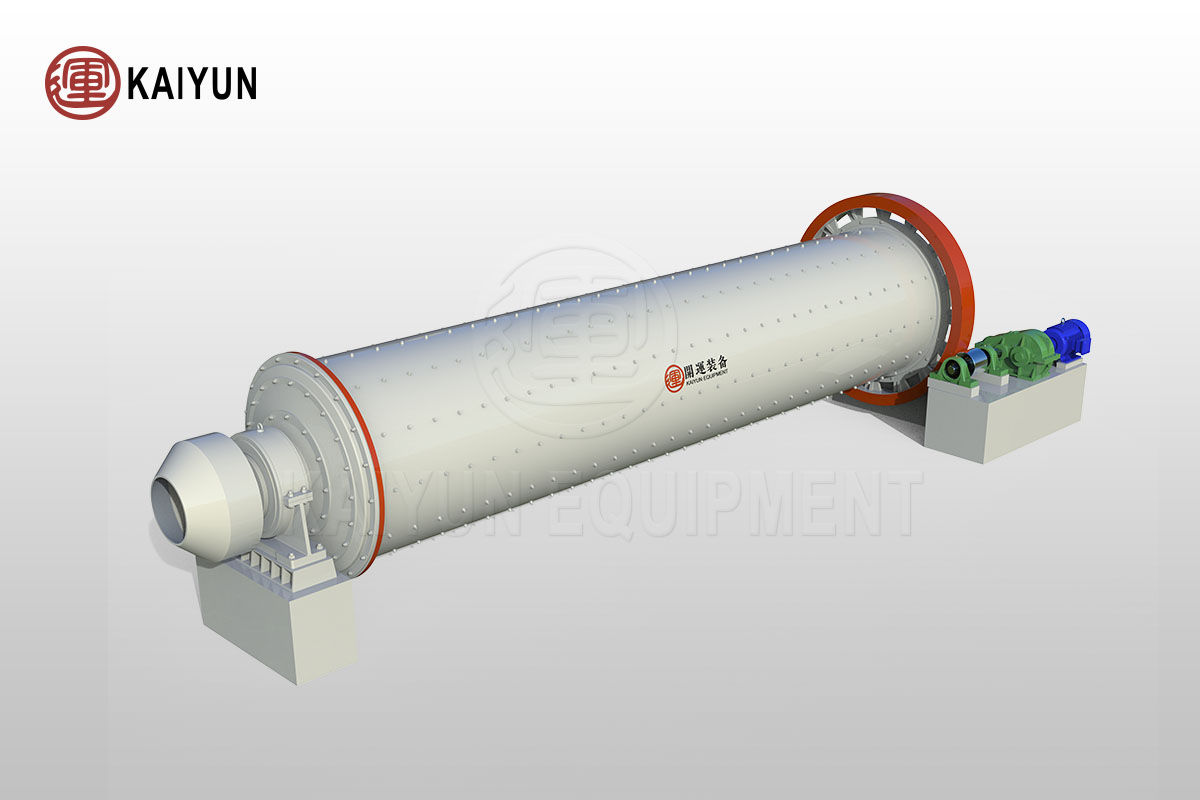
1. Crushing and grinding
Purpose: To achieve full dissociation of ore, reduce particle size, and create conditions for subsequent beneficiation.
Process flow:
(1) Crushing: The raw ore is crushed to 10-30mm by jaw crusher and cone crusher in turn.
(2) Grinding: The ore is ground to less than 0.074mm by ball mill or rod mill.
(3) Classification: The grinding product is divided into coarse and fine particles by spiral classifier, and the coarse particles are returned for re-grinding.
2. Gravity separation process
Purpose: Separate coarse ilmenite by using the specific gravity difference between ilmenite and gangue.
Equipment: Jig, spiral chute, shaking table.
Features:
(1) Efficient recovery of coarse and medium ilmenite.
(2) Simple operation and low cost.
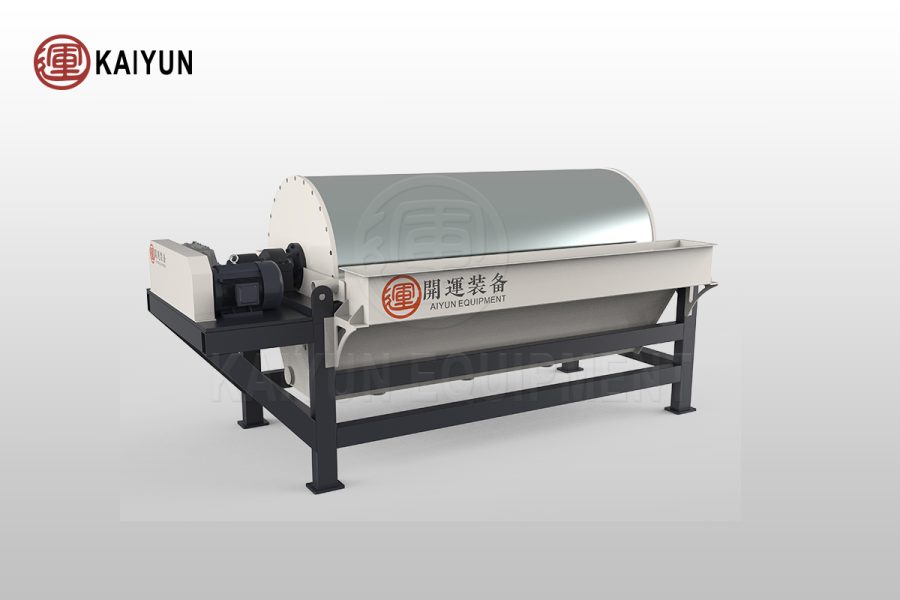
3. Magnetic separation process
Purpose: Separate ilmenite from other minerals by magnetic difference.
Equipment: High gradient magnetic separator, dry magnetic separator or wet magnetic separator.
Process flow:
(1) Low magnetic field strength: Remove strong magnetic minerals such as magnetite.
(2) High magnetic field strength: Separation of weakly magnetic ilmenite from non-magnetic gangue.
Applicability: Significant effect on ilmenite with high iron content.
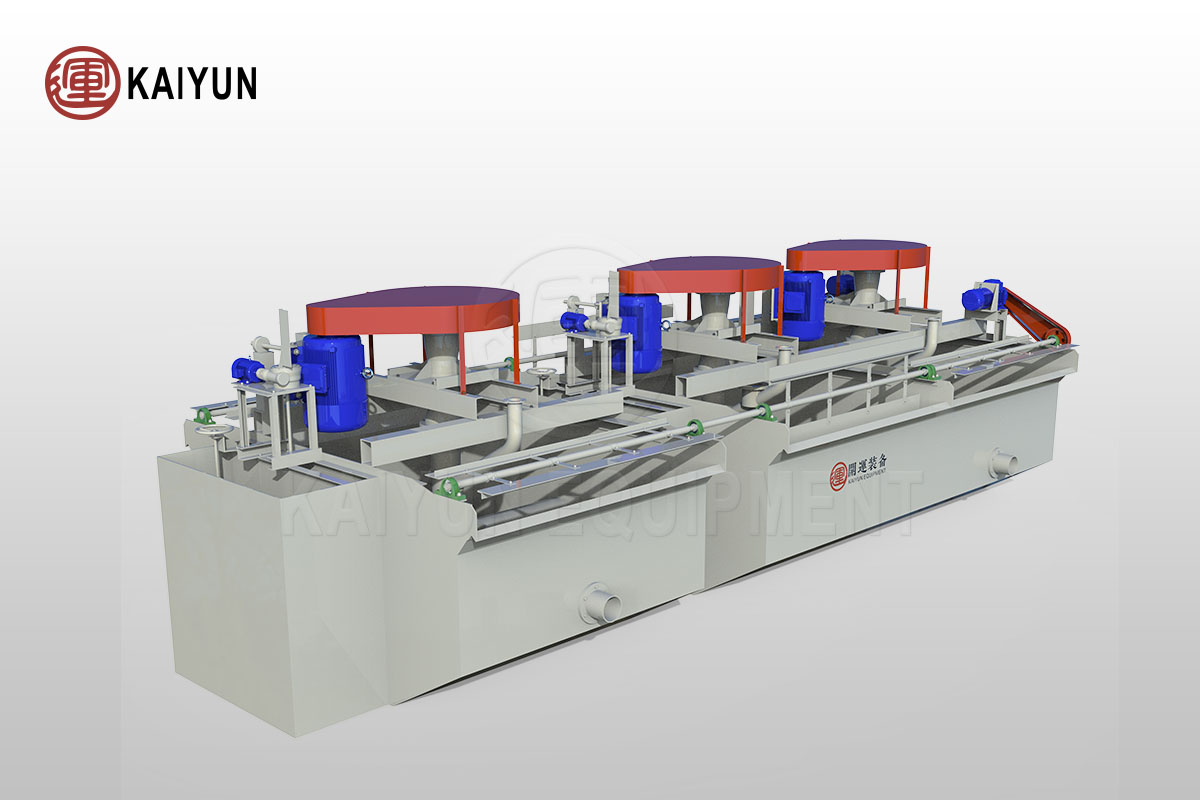
4. Flotation process
Purpose: Separate fine-grained ilmenite and improve TiO₂ grade.
Equipment: Flotation machine.
Reagents:
(1) Collectors: fatty acids, hydroxamic acids.
(2) Regulators: lime, sodium carbonate.
Process characteristics:
(1) Good effect on fine-grained minerals.
(2) Can separate ilmenite from gangue such as quartz and mica.
5. Combined beneficiation process
Characteristics: When a single process is difficult to separate efficiently, multiple processes are usually used in combination.
Typical process:
(1) Gravity-magnetic combined process: First use gravity separation to enrich, then use magnetic separation to purify.
(2) Magnetic-flotation combined process: Magnetic separation to recover coarse-grained ilmenite, and flotation to recover fine-grained minerals.
Key technologies of mineral processing
1. Ore separation: Reasonably control the grinding particle size to ensure the full separation of ilmenite and gangue.
2. Equipment selection: Select high-efficiency and energy-saving crushers, ball mills and magnetic separation equipment.
3. Reagent optimization: Select appropriate flotation reagents and dosages for different ores.
4. Environmental protection measures: Ore processing wastewater and tailings need to be properly treated to meet environmental protection requirements.