Gold Sulfide Roasting Process
Gold sulfide (Au₂S) roasting method is a high-temperature oxidation treatment method. Through high-temperature roasting, the sulfur element in the gold sulfide is converted into gaseous sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and the gold is converted into an extractable oxidized state or metallic gold. This process is mainly used for the pre-smelting treatment of gold sulfide ore or gold-containing sulfides.
Management Specifications for Mineral Processing Flowsheets
The rationality of mineral processing flowsheets directly impacts production efficiency and must be formulated based on ore testing, production practices, and practical conditions.
Gold Extraction from Carbon-in-Leaching (CIL) Process: The Key Steps from Ore to Gold Ingots
Gold extraction from carbon-in-leach (CIL) is an efficient gold extraction process that combines gold leaching with adsorption processes to reduce equipment and energy consumption and improve gold recovery.
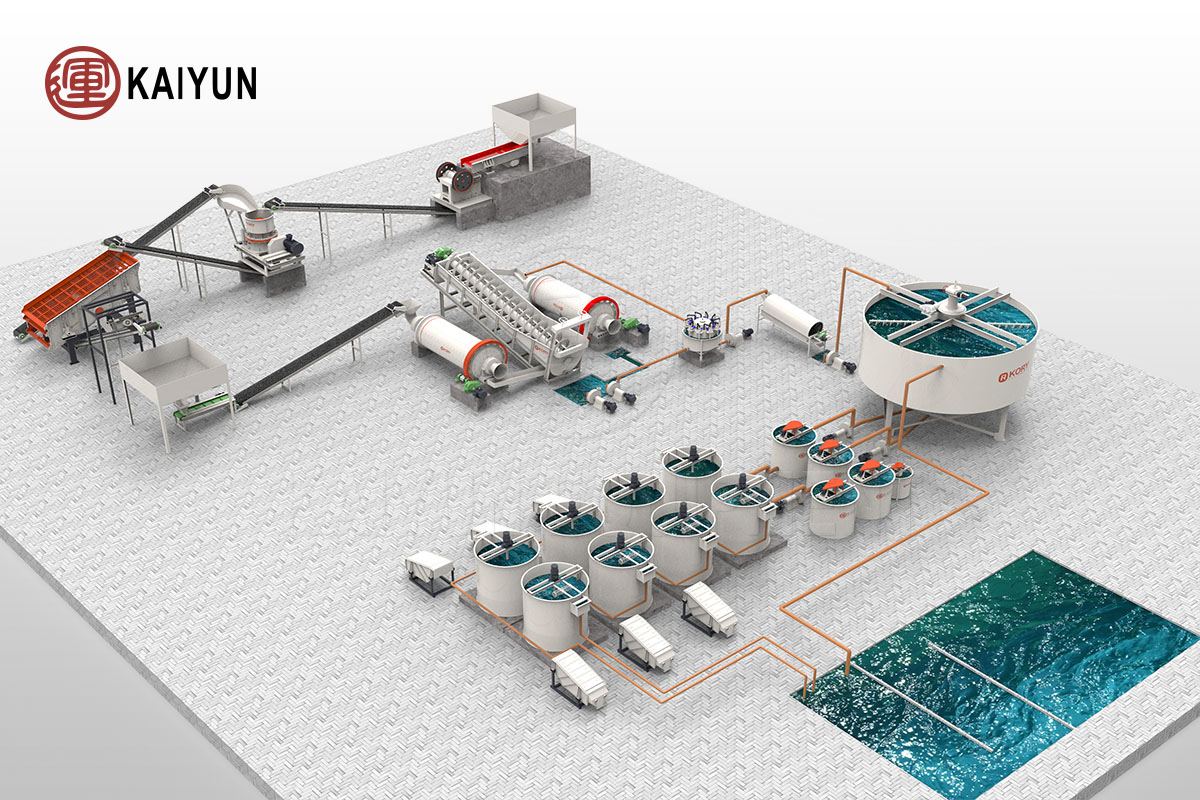
Gold Ore CIP Processing Line: Core Equipment Overview
Complete Gold Ore CIP (Carbon-in-Pulp) Processing Line covering crushing, grinding, leaching, carbon adsorption, desorption-electrolysis, and water recycling. High gold recovery rate, stable operation, lower costs, and eco-friendly design. Ideal solution for modern gold mining projects.
Core Requirements for Activated Carbon in Gold CIP Processing
Learn the core requirements for activated carbon in Gold CIP processing. Improve CIP adsorption efficiency, gold recovery, and plant stability with the right carbon selection.
Crushing in Mineral Processing: Roles, Stages, and Crusher Selection Guide
Learn the role of crushing in mineral processing, three crushing stages, and how to select the right crusher for different ores and capacities.
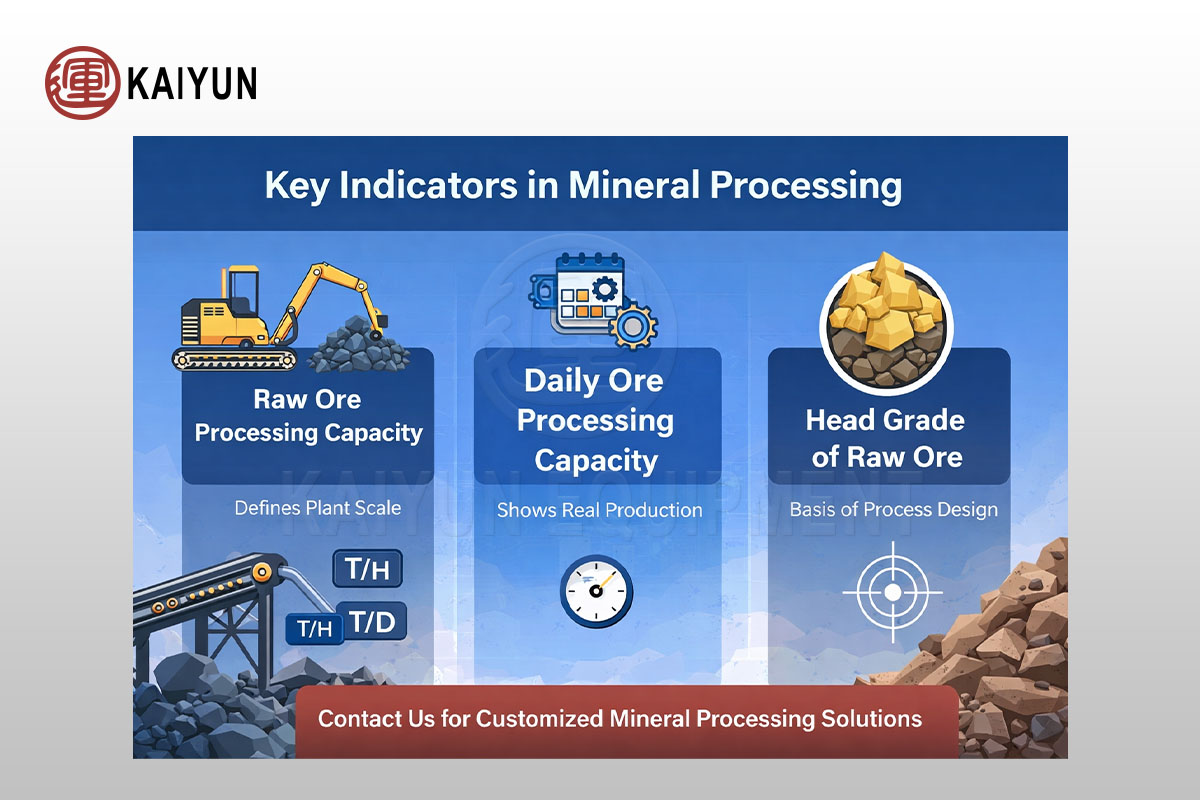
Raw Ore Processing Capacity & Head Grade | Mineral Processing Plant Design
Learn how raw ore processing capacity, daily throughput and head grade affect mineral processing plant design, equipment selection and production efficiency.
What Are Rougher, Cleaner and Scavenger Separation in Mineral Processing?
Learn the differences between rougher, cleaner and scavenger separation in mineral processing, and understand concentrate, middling and tailings in a clear flowsheet overview.
What are the basic operations typically involved in a mineral processing process?
Mineral processing involves ore preparation, separation, and dewatering—liberating minerals, separating valuables, and removing moisture for use and sale.
What are the Commonly Used Beneficiation Methods?
Beneficiation methods include physical separation by density, magnetism, or conductivity, and chemical processes such as flotation, roasting, and leaching.
What is Mineral Processing?
Mineral processing is an indispensable and crucial step in mining production. Through scientific mineral processing techniques, valuable minerals in ore are efficiently separated and enriched to provide qualified concentrate products for subsequent smelting and industrial applications.
Gold CIP vs CIL Process Detailed Comparison(II)
Gold CIP (Carbon in Pulp) and Gold CIL (Carbon in Leach) are two of the most widely used cyanide gold extraction processes. Both technologies are mature, reliable, and capable of achieving high gold recovery — when properly matched with the ore characteristics.
Gold CIP vs CIL Process Detailed Comparison(I)
Gold CIP (Carbon in Pulp) and Gold CIL (Carbon in Leach) are two of the most widely used cyanide gold extraction processes. Both technologies are mature, reliable, and capable of achieving high gold recovery — when properly matched with the ore characteristics.
Gold CIP vs CIL Process | Difference, Selection & Plant Solution
Compare Gold CIP and CIL processes. Learn key differences, applications, recovery performance, and how to choose the right gold processing solution for your ore.
Gold CIP Process | Carbon in Pulp Plant FAQs & Solutions
Gold CIP (Carbon in Pulp) processing plant for gold recovery. Learn process flow, applications, recovery efficiency, and operating cost. Request a solution now.