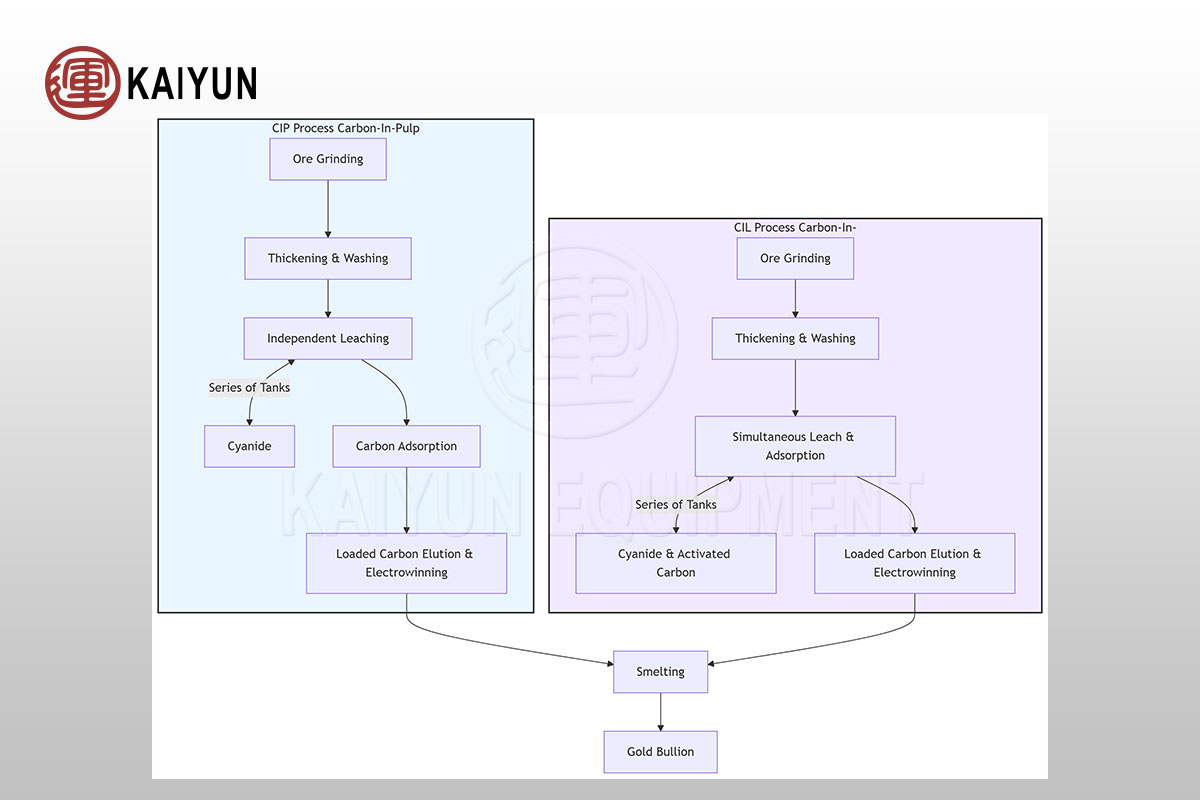
CIL vs. CIP Gold Processing: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to modern gold extraction, two of the most widely used methods are Carbon-in-Leach (CIL) and Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP). While they share similarities, there are key differences that can influence efficiency, cost, and plant design. Understanding these processes can help mining operations choose the right solution for their needs.
Mobile Crushing Stations: An Efficient and Flexible Solution for Mines and Quarries
In the mining and quarrying industries, the efficiency and flexibility of production lines directly impact a company's costs and profitability. In recent years, more and more companies have begun to focus on mobile crushing solutions as an alternative to traditional fixed production lines. The advantages of mobile production lines are particularly prominent in small quarries or deep mining environments.
Mobile Construction Waste Recycling and Crushing Stations: The Policy-Driven Tool for Green Building
In recent years, with the accelerated pace of urbanization in my country, the number of building demolition and urban renewal projects has continued to increase, leading to a surge in the amount of construction waste generated. Statistics show that construction waste now accounts for over 40% of municipal solid waste. Efficiently and environmentally friendly disposal of this waste has become a key issue for sustainable urban development. Mobile construction waste recycling and crushing stations, with their flexibility, high processing efficiency, and controllable recycled aggregate quality, are becoming a key component of "zero-waste" construction sites.
Cone Crusher–The Efficient Choice for Fine Crushing of Medium and High Hardness Materials
In the mining and aggregate industry, materials such as granite and basalt are known for their high hardness, which makes crushing a challenge. The traditional jaw crusher + impact crusher two-stage process is common, but when dealing with ores with a compressive strength of ≥250 MPa, it often suffers from fast wear, insufficient capacity, and high maintenance costs.
Cone Crusher:Common Faults and Troubleshooting Methods
Cone crusher, as secondary or tertiary crushing equipment in mining and sand and gravel aggregate production, are widely used due to their high crushing ratio, high efficiency, and fine particle size. However, over time, cone crushers can experience various malfunctions.
Detailed Explanation of Sand and Gravel Aggregate Particle Size and Mesh Count
In sand and gravel aggregate production, construction projects, and concrete mixing, particle size and mesh count are important indicators of aggregate quality. Understanding their meaning and relationship not only helps select the right materials but also improves project quality and production efficiency.
Jaw Crusher Troubleshooting and Maintenance Guide
The jaw crusher is the most common primary crushing equipment used in mines, mineral processing plants, sand and gravel yards, and construction aggregate production lines. It is popular for its simple structure, high crushing ratio, and high output. However, due to its high operating inertia, heavy loads, hard materials, and harsh operating environment, various malfunctions are inevitable over time.
Jaw Crusher Safety Mechanism and Discharge Opening Adjustment
The toggle plate of a jaw crusher serves not only to transmit power and drive the movable jaw to swing back and forth, but also as a safety device and a means for discharge opening adjustment.
What is the CIP Process in Gold Mining? The Complete Guide to Carbon-in-Pulp Gold Extraction
CIP (Carbon-in-Pulp) is a gold cyanidation process where gold is leached from ore and then adsorbed onto activated carbon suspended in the pulp. It differs from the CIL (Carbon-in-Leach) process mainly in that the leaching and carbon adsorption steps are done sequentially, rather than simultaneously.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- Next Page »