Product Introduction
The disk feeder, designed for the continuous feeding of powdery materials, excels in delivering non-cohesive materials evenly.
The disk feeder plays a crucial role in industries such as mining, metallurgy, cement, sand mining, and mechanized casting workshops.
Whether suspended from steel structures or installed below hoppers, it ensures continuous and stable material supply.
Particularly suited for powdery materials with poor flowability, the disk feeder provides precise control and efficiency in the feeding process, although it is not ideal for materials with very good flowability.
Table of Contents
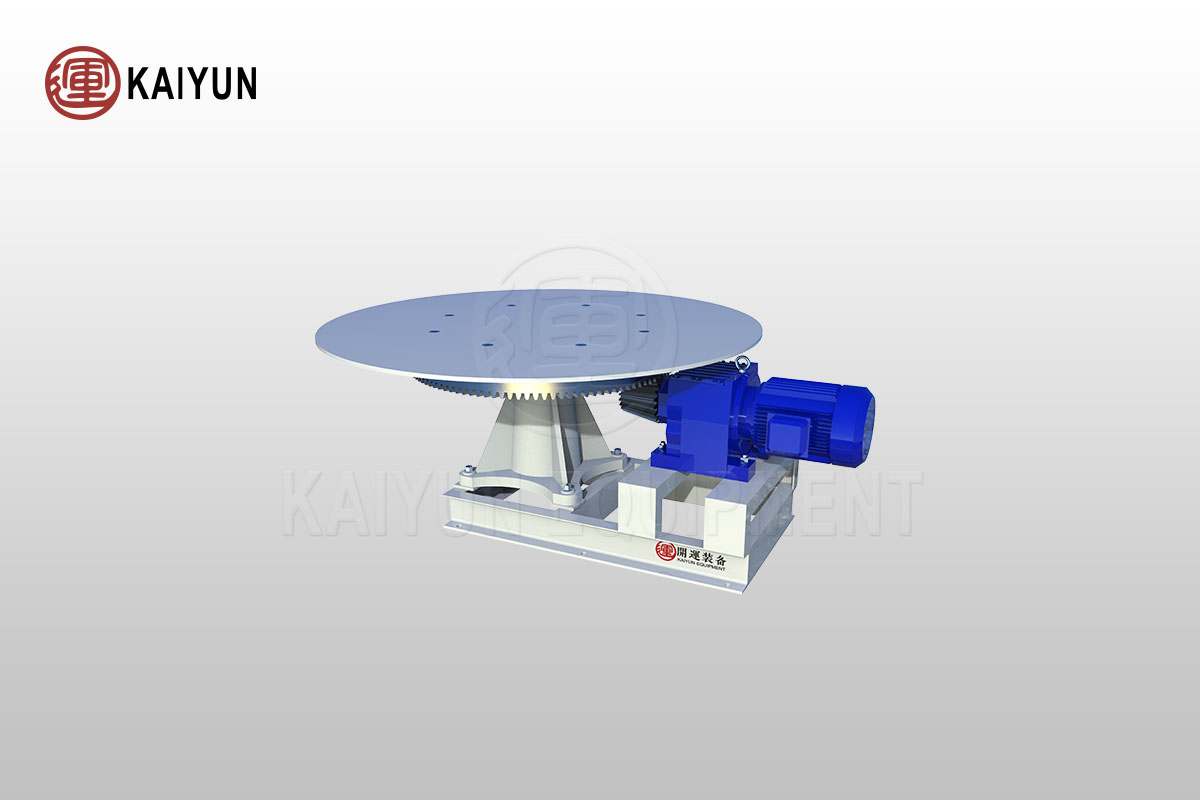
Advantages and Features
Stable Operation, Simple Operation
The disk feeder’s straightforward design and intuitive operation ensure stable performance and ease of use. This reduces the learning curve for operators and enhances production efficiency.
Wide Applicability, Energy Efficiency
Suitable for various industrial scenarios, it effectively handles different non-cohesive materials while demonstrating excellent energy efficiency. This reduces production costs and enhances economic benefits.
High Load Capacity, Smooth Operation
Its robust load-bearing capacity and smooth operation characteristics ensure continuous and even material feeding, providing a solid foundation for stable subsequent processes.
Streamlined Design, Uniform Feeding
The simple structure not only facilitates maintenance but also ensures uniform material supply, improving the reliability of the production process.
Working Principle
The core working principle of the disk feeder revolves around its unique material feeding mechanism. Bulk materials are first loaded from the hopper into the receiving cylinder, relying on gravity to form a stockpile on the disk. By adjusting the adjusting bolts, the gap between the sleeve and the disk is controlled, which in turn adjusts the natural pile angle of the material on the disk, achieving precise control of the feeding amount.
As the disk rotates, the discharge blade evenly scrapes material off the disk. With the continuous rotation of the disk, the material is continuously and evenly scraped into the receiving hopper, completing the feeding operation. Notably, by adjusting the gap between the discharge blade and the disk, further control of the feeding amount can be achieved, allowing for precise regulation of the feeding process.
Technical parameters
| Model | Disc diameter (mm) | Disc speed (r/min) | Upper limit feeding size (mm) | Feeding capacity (t/h) | Motor model | Motor power (kw) | Weight (kg) |
| DF600 | 600 | 7. 53 | 25 | 1. 8-3. 9 | Y90L- 6 | 1. 1 | 410 |
| DF800 | 800 | 7. 53 | 30 | 3. 5-7. 6 | Y90L- 6 | 1.1 | 600 |
| DF1000 | 1000 | 7. 50 | 40 | 1.8-16.7 | Y100L- 6 | 1. 5 | 725 |
| DF1300 | 1300 | 6. 5 | 50 | 4. 3-27. 9 | Y132S- 6 | 3 | 846 |
| DF1600 | 1600 | 6 | 60 | 7.03-48.6 | Y132M1- 6 | 4 | 1980 |
| DF1800 | 1800 | 5 | 70 | 9.26-60 | Y132M2- 6 | 5.5 | 3070 |
| DF2000 | 2000 | 5 | 80 | 13.6-88.4 | Y132M2- 6 | 5.5 | 3260 |